Very Short Questions
Question 1. What is a journal?
Solution 1: Journal is a book of prime entry or a book of original entry in which transaction are first recorded in a chronological order or sequence they are entered. Journal is called the Book of Original Entry since all transactions are initially recorded in it.
Question 2. Why is the journal called a book of original entry?
Solution 2: All the transactions are recorded firstly in the journal so it is called book of original entry.
Question 3. What is journalising?
Solution 3: The method of recording the transaction in the journal is called journalising.
Question 4. Give one advantage of journal.
Solution 4: Recording of accounting data in chronological order is the advantage of journal.
Question 5. Give one limitation of a journal.
Solution 5: It is impossible to record all the heavy and bulky transactions are the only limitation of journal.
Question 6. What is a narrative?
Solution 6: All the transaction has a brief description after each entry is known as narrative.
Question 7. What is ledger folio or L.F.?
Solution 7: Ledger folio or L.F. is the page number where the journal is posing made. The page number is recorded in the journal.
Question 8. What is compound journal entry?
Solution 8: When two or more transactions related to one particular account take place on the same date. In this situation, instead of recording separate entries only one entry is passed. This type of journal entry is known as compound journal entry.
Question 9. What is opening entry?
Solution 9: The first entry in the Journal is passed to record closing balances of the previous year. It is called the opening entry. The Balance Sheet prepared at the end of the year shows the closing balances of each asset and liability and forms the basis for this opening entry.
Question 10. What entry is passed for withdrawing of goods by the proprietor for personal use?
Solution 10: Drawings A/c Dr.
To Purchase A/c
Question 11. Which account should be debited, if wages are paid for the installation of a machine?
Solution 11: Machine account.
Practical Questions
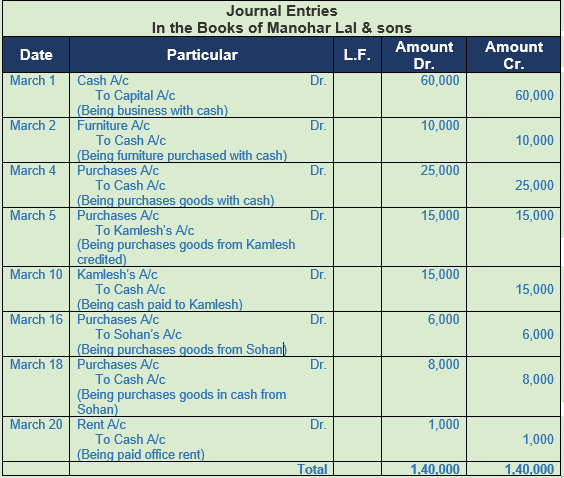
Question 1. Prepare a journal of Manohar Lal & sons from the following transactions:-
2018 Amount
March 1 Manohar Lal & Sons started a business with cash 60,000
March 2 Purchased furniture for cash 10,000
March 4 Purchased goods for cash 25,000
March 5 Bought goods from Kamlesh 15,000
March 10 Paid cash to Kamlesh 15,000
March 16 Purchased goods from Sohan 6,000
March 18 Purchased goods from Sohan for cash 8,000
March 20 Paid rent for the office 1,000
Solution 1:
Point of Knowledge:-
Journal is a book of prime entry or a book of original entry in which transaction are first recorded in a chronological order or sequence they are entered. Journal is called the Book of Original Entry since all transactions are initially recorded in it.
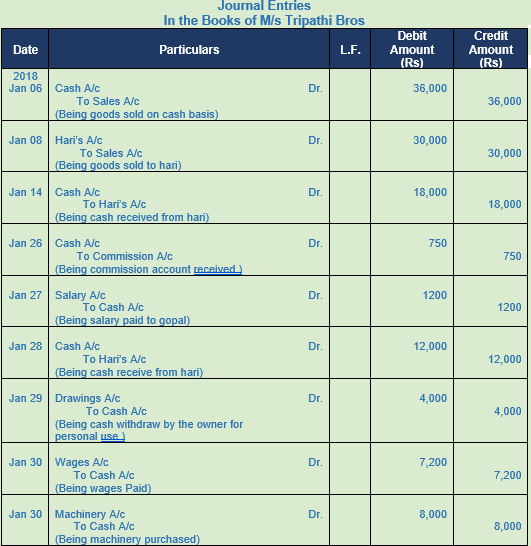
Question 2. Prepare Journal of M/s Tripathi Bros from the following transactions:-
2018 Amount
Jan. 6 Sold goods for Cash 36,000
Jan. 8 Sold goods to Hari 30,000
Jan. 14 Received cash from Hari 18,000
Jan. 26 Received Commission 750
Jan. 27 Paid Salary to Gopal 1200
Jan. 28 Received cash from Hari 12,000
Jan. 29 Withdrew cash from office personal use 4,000
Jan. 30 Wages paid 7,200
Jan. 30 Bought Machinery for cash 8,000
Solution 2:
Working Note:-
The first entry in the Journal is passed to record closing balances of the previous year. It is called the opening entry. The Balance Sheet prepared at the end of the year shows the closing balances of each asset and liability and forms the basis for this opening entry.
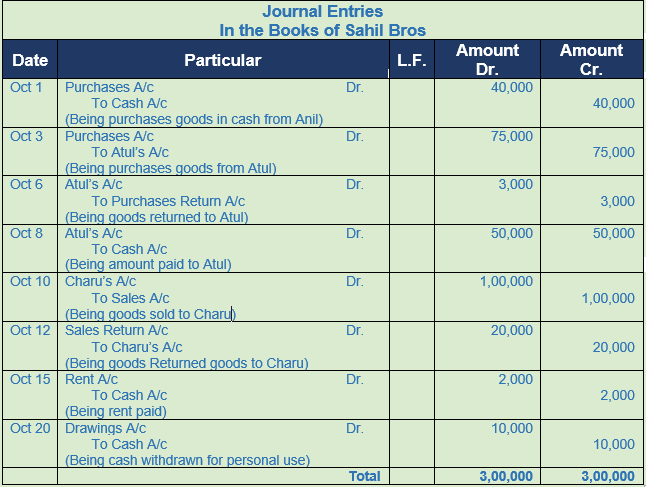
Question 3. Prepare Journal of Sahil Bros. from the following transactions:-
2016 Amount
Oct.1 Purchased goods from Anil for cash 40,000
Oct.3 Purchased goods from Atul 75,000
Oct.6 Returned goods to Atul 3,000
Oct.8 Paid cash to Atul 50,000
Oct.10 Sold goods to Charu 1,00,000
Oct.12 Charu returned 20% of goods
Oct.15 Paid rent 2,000
Oct.20 Sahil withdrew for personal use 10,000
Solution 3:
Working Note:-
1.) Total Sales to Charu = 1,00,000
Sales Return = Rs. 1,00,000 × 20% = Rs. 20,000
Point of the Knowledge:-
- Capital Account is debited when there is a decrease in capital.
- Capital Account is credited when there is a increase in capital.
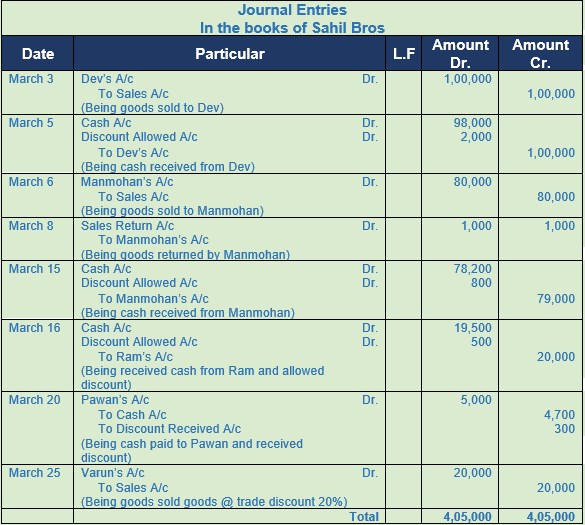
Question 4. Enter the following transactions in the Journal of Ganesh Bros.
2017 Amount
March 3 Sold goods to Dev 1,00,000
March 5 Received from Dev in full settlement of his account 98,000
March 6 Sold goods to Manmohan 80,000
March 8 Manmohan returned goods 1,000
March 15 Received from Manmohan in full settlement of his account 78,200
March 16 Received cash from Ram 19,500
discount allowed 500
March 20 Paid cash to Pawan and discount received from him 4,700
March 25 Sold goods to Varun of the list price of Rs. 25,000 at 20% trade discount
Solution 4:
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 25,000
Trade discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 25,000 × 20% = Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 25,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000
Point of Knowledge:-
The following are the two advantages of Journal.
- Recording of accounting data in chronological order.
- Narration of journal explains the transactions very well.
Question 5. Pass Journal entries in the books of Hari Shankar & Co. from the following:-
2017 Amount
April 1 Commenced business with cash 50,000
April 2 Purchased goods from Subhash 20,000
April 4 Sold goods to Ramnath 15,000
April 6 Ramnath returned defective goods 1,000
April 10 Received cash from Ramnath and 13,800
Discount allowed 200
April 12 Gopal sold goods to us 10,000
April 14 Paid to Gopal in full settlement of his account after 5% discount.
April 15 Paid Rent 10,000
April 16 Paid Rent of Hari Shankar’s residence 5,000
April 18 Purchased goods for cash from Govind for Rs. 6,000 at 20% trade discount.
April 20 Purchased goods from Govind for Rs. 10,000 at 20% trade discount.
April 24 Paid to Govind Rs. 7,850 in full settlement of his account.
April 25 Paid to Subhash Rs. 4,750; discount received Rs. 250.
April 30 Paid Wages Rs. 400; Salaries Rs. 4,000; Advertisement expenses Rs. 800 and Trade expenses Rs. 1,000
Solution 5:
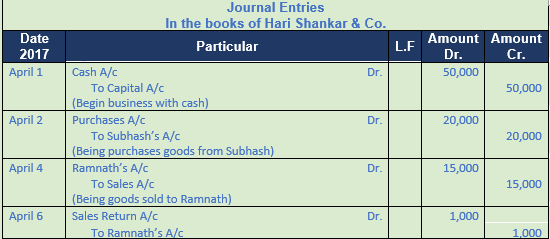
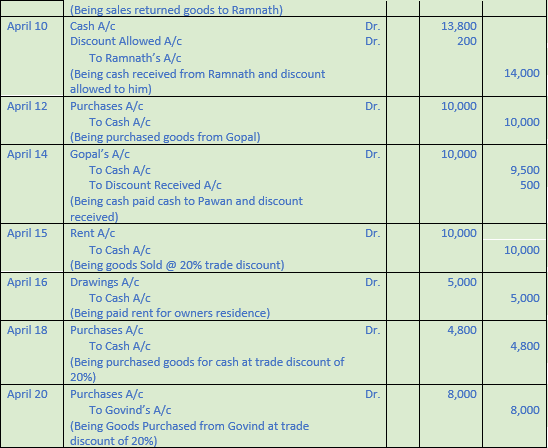
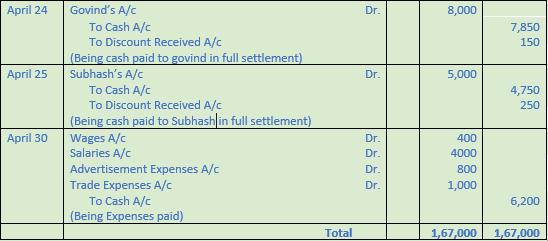
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of discount
Discount Amount = Rs. 10,000 × 5% = Rs. 500
Amount paid to Gopal = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 500
= Rs. 9,500
Point of knowledge:-
Trade Discount is allowed by the seller on purchase of goods in large quantity. It is usually by the wholesalers to the retail shop owners who further sell the goods to the consumer. Trade Discount is deducted in the invoice from sale price and is not recorded in the books of account. Sales are recorded at net sales price or sale price less trade discount. GST or CGST, SGST and IGST are levied on the net sale price. Trade discount is allowed on sales, hence it is allowed on both cash and credit sales.
Question 6. Prepare a journal of Maruti nandan stores
2017
Oct 1 Purchased goods from Ghanshyam of the list price of Rs. 50,000 at 15% trade discount.
Oct 3 Returned goods to Ghanshyam of the list price of Rs. 2,000
Oct 6 Paid cash to Ghanshyam Rs. 40,000 in full settlement of his account
Oct 8 Purchased goods from Raghu of the list price of Rs. 60,000 at 10% trade discount.
Oct 10 Returned goods to Raghu of the list price of Rs. 5,000.
Oct 12 Paid cash to Raghu Rs. 49,000 in full settlement of his account.
Solution 6:
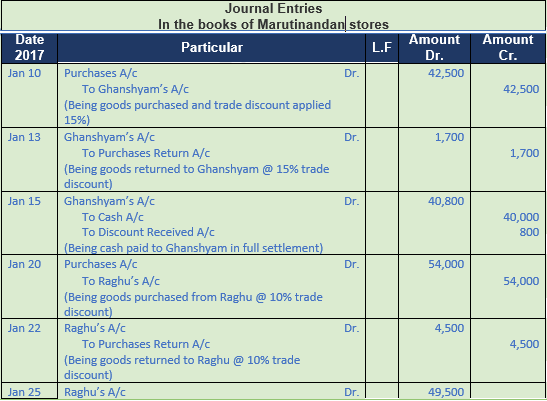
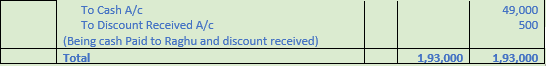
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 50,000
Trade discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 50,000 × 15% = Rs. 7,500
Sales = Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 7,500
Sales = Rs. 42,500
2.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 60,000
Trade discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 60,000 × 10% = Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 54,000
Point of knowledge:-
The following are the two advantages of allowing Trade Discount:
1.) Increased sales due to high quantity involved in sales.
2.) Increased customer base due to low prices and discount offers.
Question 7. Prepare a journal of the following transaction
2017
Jan 6 Sold goods to Muskan of the list price of Rs. 2,00,000 at trade discount of 20%
Jan 8 Muskan returned goods of the list price of Rs. 5,000
Jan 15 Received from Muskan the full payment under a cash discount of 4%
Solution 7:
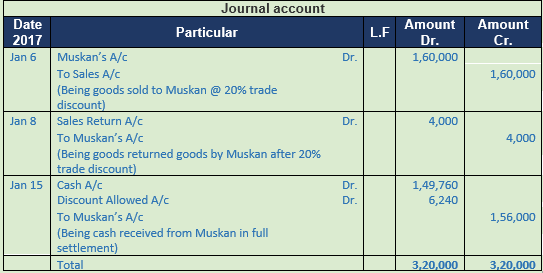
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 2,00,000
Trade discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,00,000 × 20% = Rs. 40,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 40,000
Sales = Rs. 1,60,000
Point of Knowledge:-
Cash Discount is allowed by the seller to the customers to encourage prompt or early payment. It is allowed as a per cent of invoice value or payment made say @ 5% of invoice value to the buyer. Cash discount is calculated after deducting trade discount from the invoice price. Cash discount is calculated always on net amount. It is allowed at the time of receipt of amount in cash or by cheque.
Question 8. Prepare a journal of the following transaction of Raja Ram
2017
March 3 Bought goods for cash of the list price of Rs. 80,000 at 10% trade discount and 2% cash discount.
March 5 Sold goods for cash of the list price of Rs. 1,00,000 at 15% trade discount and 3% cash discount.
March 6 Sold goods to Nagpal of the list price of Rs. 50,000 at 20% trade discount.
March 8 Nagpal returned one-fourth of the above goods
March 10 Nagpal settled the account by paying cash under a discount of 5%
Solution 8:
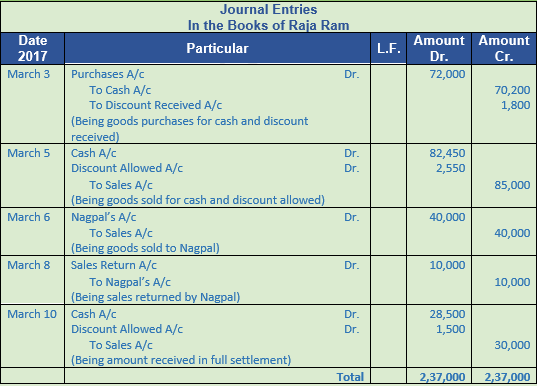
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 80,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 80,000 × 10% = Rs. 8,000
Sales = Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 8,000
Sales = Rs. 72,000
Cash discount = 2.5%
Discount amount = Rs. 72,000 × 2.5%
= Rs. 1,800
Amount Received = Rs. 72,000 – Rs. 1,800
= Rs. 70,200
Point of knowledge:-
- Recording of accounting data in chronological order.
- Narration of journal explains the transactions very well.
Question 9. Prepare a journal entry.
2016
Mar 5 Sold goods to Shruti for Rs. 80,000 at 15% trade discount and 4% cash discount. Received 75% amount immediately through a cheque
Mar 10 Purchased goods from Richa for Rs. 60,000 at 10% trade discount and 5% cash discount. 60% amount paid by cheque immediately
Solution 9:
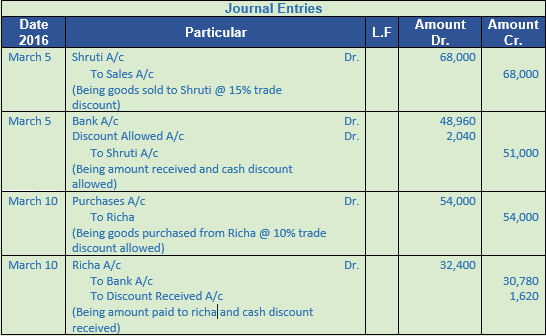
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of selling price
List price = Rs. 80,000
Trade Discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 80,000 × 15% = Rs. 12,000
Sales = Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 12,000
Sales = Rs. 68,000
Amount received in cash = Rs. 68000 × 75%
= Rs. 51,000
Cash discount = 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 51,000 × 4%
= Rs. 2,040
Amount Received = Rs. 51,000 – Rs. 2,020
= Rs. 48,960
2.) Calculation of purchases price
List price = Rs. 60,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 60,000 × 10% = Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 60,000 – Rs. 6,000
Sales = Rs. 54,000
Amount received in cash = Rs. 54,000 × 60%
= Rs. 32,400
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 32,400 × 5%
= Rs. 1,620
Amount Received = Rs. 32,400 – Rs. 1,620
= Rs. 30,780
Question 10. Prepare a journal entry
2017
Jan 6 Purchased goods from Henry for Rs. 50,000 on 10% trade discount and 4% cash discount and paid 60% amount by cheque.
Jan 15 Bought goods from Amit for Rs. 2,00,000 at terms 5% cash discount and 20% trade discount. Paid 3/4th of the amount in cash at the time of purchase.
Jan 18 Sold goods to Sherpa at the list price of Rs. 50,000 less 20% trade discount and 4% cash discount if the payment is made within 7 days. 75% payment is received by cheque on Jan. 23rd
Jan 25 Sold goods to Garima for Rs. 1,00,000, allowed her 20% trade discount and 5% cash discount if the payment is made within 15 days. She paid 1/4th of the amount by cheque on Feb. 5th and 60% of the remainder on Feb.15th in cash
Solution 10:
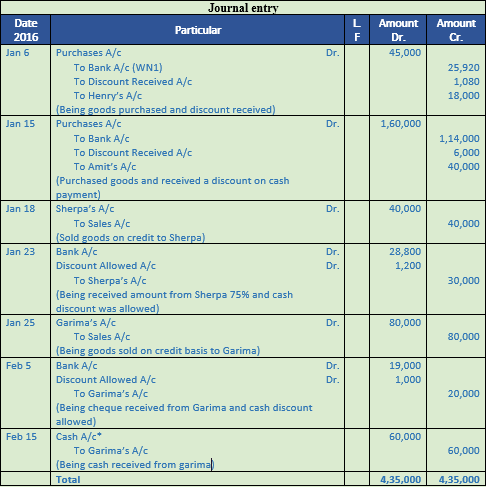
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid to hanry:-
List price = Rs. 50,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 50,000 × 10% = Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 45,000
Amount received in cash = Rs. 45,000 × 60%
= Rs. 27,000
Cash discount = 4%
Discount amount = Rs. 27,000 × 4%
= Rs. 1,080
Amount Received = Rs. 27,000 – Rs. 1,080
= Rs. 25,920
Question 11. 2017
March Particulars
2 Sold goods to Dilip of the list price of Rs. 62,000 for Rs. 60,000.
5 Sold goods to Amrit Lal of the list price of Rs. 2,50,000 at 20% trade discount and 10% cash discount. Amrit Lal paid Rs. 1,20,000 immediately through a banker’s cheque.
10 Paid cheque of Rs. 30,000 to Chaturvedi and availed discount 2%.
16 Purchased goods costing Rs. 2,00,000 from Hari & Co. Paid 75% immediately by cheque to avail 4% discount.
20 Sold goods to Vhsal Traders costing Rs. 40,000 at 25% profit, allowing 10% trade discount and 10% cash discount. Received 80% payment immediately by cheque.
26 Sold goods to Brij & Co. costing Rs. 50,000 at 40% profit, allowing 10% trade discount and 5% cash discount. Brij & Co. paid the full amount by cheque and availed cash discount.
Solution 11:
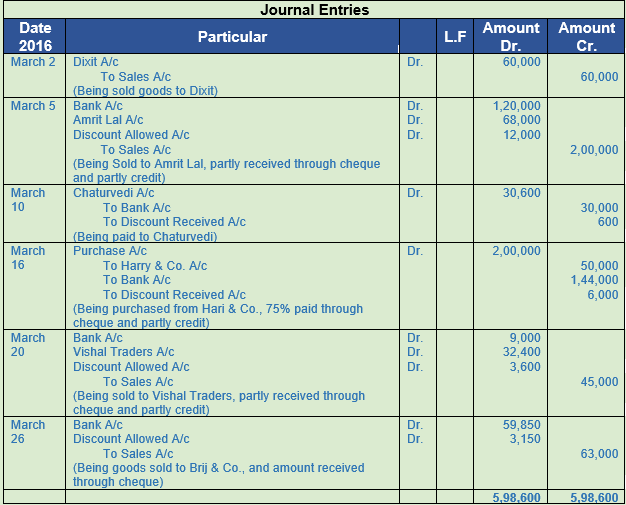
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 2,50,000
Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,50,000 × 20% = Rs. 50,000
Sales = Rs. 2,50,000 – Rs. 50,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000
Amount received in cash = Rs. 1,20,000
Cash discount = 10%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,20,000 × 10%
= Rs. 12,000
Amount Received = Rs. 1,20,000 – Rs. 12,000
= Rs. 1,08,000
Point of Knowledge:-
Trade Discount is allowed by the seller on purchase of goods in large quantity. It is usually by the wholesalers to the retail shop owners who further sell the goods to the consumer. Trade Discount is deducted in the invoice from sale price and is not recorded in the books of account.
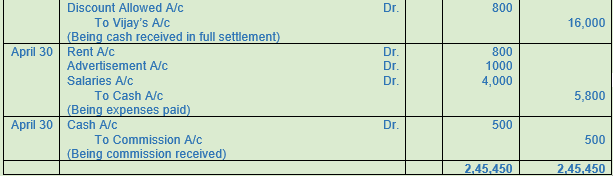
Question 12. Enter the Shyam Sunder & Sons transactions in their Journal.
2017
April Particulars
1 Shyam Sunder & Sons started a business with Cash Rs. 75,000; Goods Rs. 30,000 and Furniture Rs. 5,000.
2 Sold goods to Bhushan of the list price of Rs. 10,000 at a trade discount of 10%.
5 Paid cheque of Rs. 30,000 to Chaturvedi and availed discount 2%.
10 Received from Bhushan Rs. 8,000 in full settlement of his account.
12 Purchased Furniture for Rs. 6,000.
Purchased goods from Navin for Rs. 25,000 less trade discount 12%
15 Returned goods to Navin goods of the list price of Rs. 2,000.
16 Cleared the account of Navin by applying cash, under a discount of 5%.
17 Sold goods to Ajay Rs. 10,000 and Vijay Rs. 16,000.
20 Received cash from Ajay Rs. 9,800 in full settlement of his account. Paid insurance premium Rs. 750.
22 Paid for Shyam Sunder’s Life Insurance Premium Rs. 1,200.
24 Purchased goods for Rs. 8,000 for cash at a trade discount of 10% and a cash discount of 2%.
25 Received cash from Vijay at a cash discount of 5% in full settlement of his account.
30 Paid Rent Rs. 800; Advertisement Rs. 1,000; and Salaries Rs. 4,000.
30 Received Commission Rs. 500.
Solution 12:
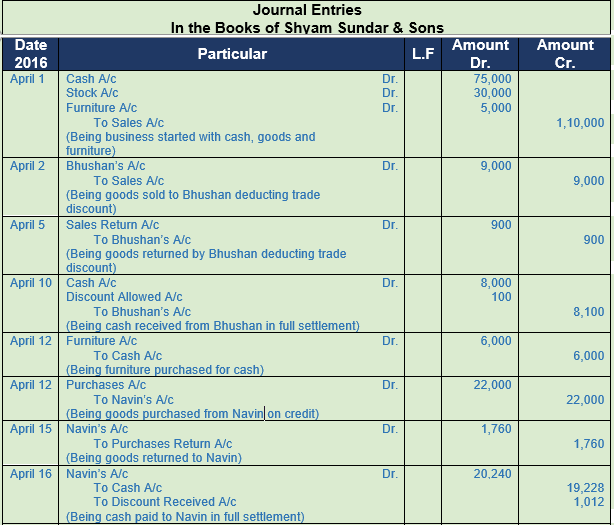
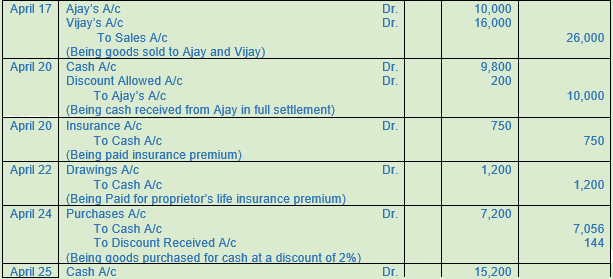
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid by bhushan:-
List price = Rs. 10,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 1,00,000 × 10% = Rs. 1,000
Sales = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 1,000
Sales = Rs. 9,000
Point of Knowledge:-
Trade Discount is allowed by the seller on purchase of goods in large quantity. It is usually by the wholesalers to the retail shop owners who further sell the goods to the consumer. Trade Discount is deducted in the invoice from sale price and is not recorded in the books of account.
Cash Discount is allowed by the seller to the customers to encourage prompt or early payment. It is allowed as a per cent of invoice value or payment made say @ 5% of invoice value to the buyer. Cash discount is calculated after deducting trade discount from the invoice price.
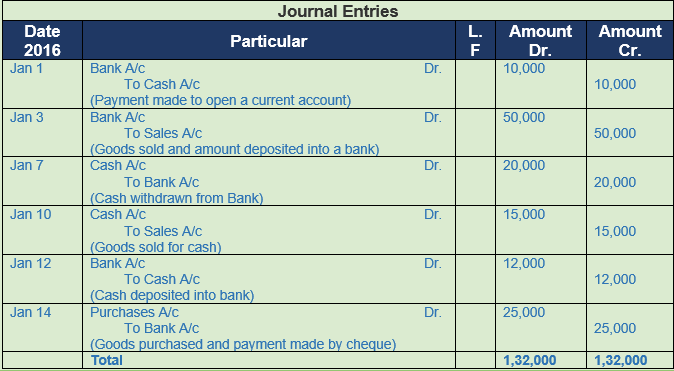
Question 13. Prepare a journal entry:-
2017 Amount
Jan 1 Paid into the bank to open a Current Account 10,000
Jan 3 Goods sold for Rs. 50,000 and the amount was deposited into the bank
Jan 7 The amount is withdrawn from a bank 20,000
Jan 10 Goods sold for Cash 15,000
Jan 12 The amount deposited into bank 12,000
April 14 Goods purchased and payment made by cheque 25,000
Solution 13:
Point of knowledge:-
1. Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
2. Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
3. Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
4. Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
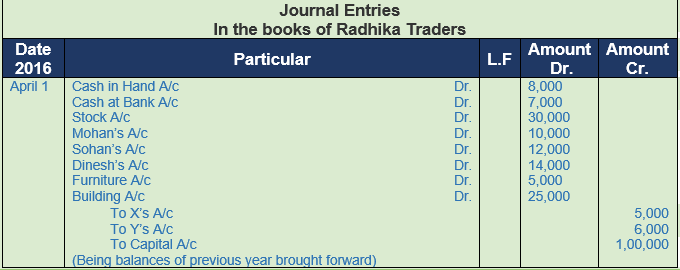
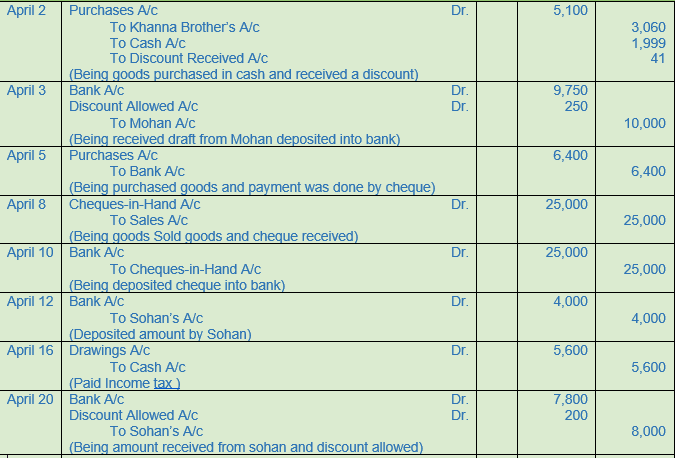
Question 14.
(A) Following balances appeared in the books of Radhika Traders as on 1st April, 2017:−
Assets: Cash Rs. 8,000; Cash at Bank Rs. 7,000; Stock Rs. 30,000; Debtors : Rs. 36,000 (Mohan Rs. 10,000; Sohan Rs. 12,000; Dinesh Rs. 14,000); Furniture Rs. 5,000; Building Rs. 25,000.
Liabilities: Creditors− X Rs. 5,000; Y Rs. 6,000.
In April, 2017, the following transaction took place:

Solution 14: (A)
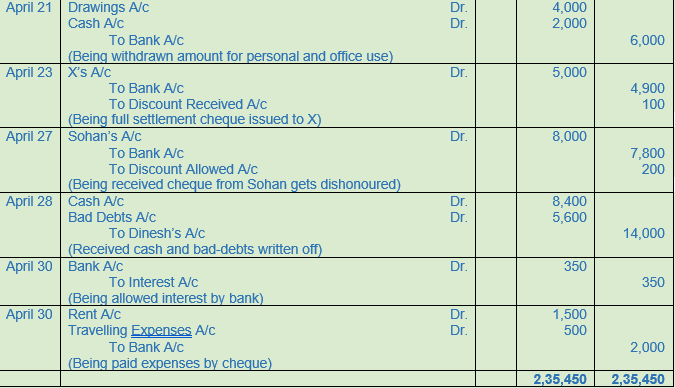
Working Note:-
1.) Calculation of amount paid by bhushan:-
List price = Rs. 8,000
Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 8,000 × 20% = Rs. 1,600
Sales = Rs. 8,000 – Rs. 1,600
Sales = Rs. 6,400
Point of Knowledge:-
1.) Increased sales due to high quantity involved in sales.
2.) Increased customer base due to low prices and discount offers.
Question 14.
(B) Following was the position of Harish & Co. as on 1st April, 2017 :−
Cash in Hand Rs. 10,000; Cash at Bank Rs. 16,800; Furniture Rs. 8,000; Stock Rs. 50,000; Debtors− Ram Rs. 8,000; Shyam Rs. 12,000; Creditors− Anil Rs. 4,000; Sunil Rs. 5,000.
Following transactions took place during April, 2017 :−
2017
April 2 Received a cheque from Ram in full settlement of his account after deducting 5% cash discount.
April 4 Deposited the above cheque into Bank.
April 5 Goods purchased for Rs. 20,000 at 10% trade discount and 5% cash discount. Payment made by cheque.
April 6 Received a cheque from Shyam for Rs. 3,860 and discount allowed to him Rs. 140. Cheque deposited into the bank on the same day.
April 10 Cash paid to Anil after deducting 2% cash discount.
April 15 Old furniture sold for Rs. 800.
April 16 Sold goods to Shiv Parshad of the list price of Rs. 10,000 at a trade discount of 15%.
April 18 Shiv Parshad returned goods of the list price of Rs. 1,000.
April 20 Paid for furniture repairs to Bahadur Singh Rs. 100.
April 25 Received a cheque from Shiv Parshad after deducting 4% cash discount. Cheque was deposited into bank.
April 28 Bank charged Rs. 50 for ‘Bank Charges’.
April 30 Received Commission Rs. 200.
Solution 14: (B)
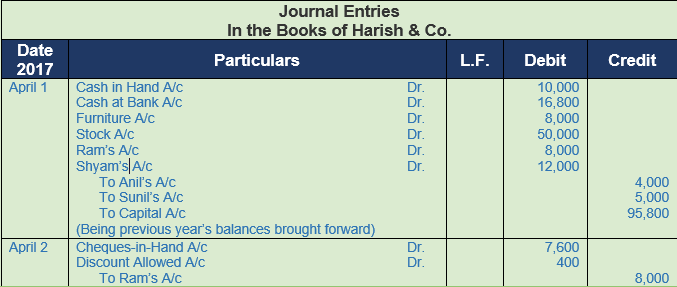
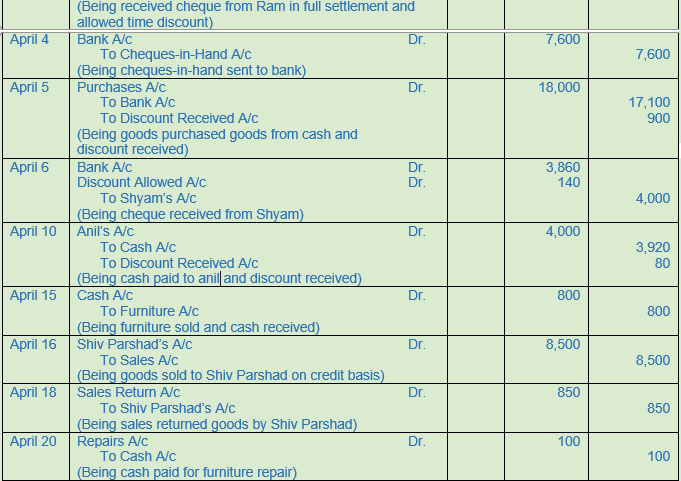
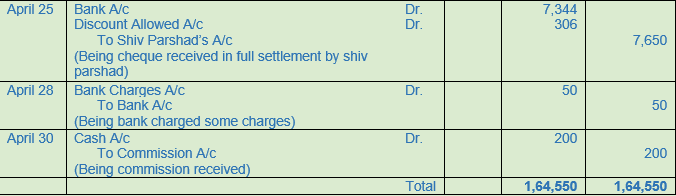
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 20,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 20,000 × 10% = Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 18,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 18,000 × 5%
= Rs. 900
Amount Received = Rs. 18,000 – Rs. 900
= Rs. 17,100
Point of Knowledge:-
Trade Discount is allowed by the seller on purchase of goods in large quantity. It is usually by the wholesalers to the retail shop owners who further sell the goods to the consumer. Trade Discount is deducted in the invoice from sale price and is not recorded in the books of account.
Cash Discount is allowed by the seller to the customers to encourage prompt or early payment. It is allowed as a per cent of invoice value or payment made say @ 5% of invoice value to the buyer. Cash discount is calculated after deducting trade discount from the invoice price.
Question 15. Pass Journal Entries
- Provide depreciation on Furniture Rs. 500 and on Machinery Rs. 2,000.
- Received cash Rs. 1,000 for bad-debts written off last year.
- Ajay Singh was declared bankrupt. He owed Rs. 2,500 to us. Nothing could be recovered from his estate.
- Rs. 20,000 for wages and Rs. 4,000 for salaries are outstanding.
- Purchased furniture for Rs. 6,000 for the proprietor and paid the amount by cheque.
- Provide 9% interest on capital amounting to Rs. 2,00,000.
- Charge interest on drawings Rs. 1,000.
Solution 15:
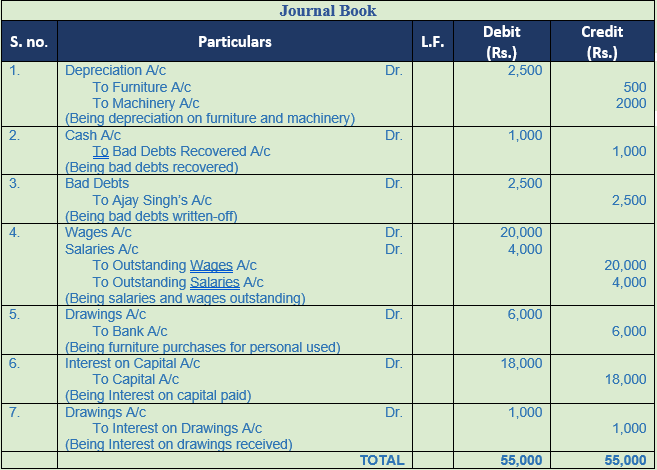
Point of knowledge:-
- Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
- Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
Question 16. Pass Journal Entries
2017
Jan 5 Purchased goods for Cash Rs. 10,000 and spent Rs. 200 for their carriage
Jan 10 Purchased machinery for Cash Rs. 50,000 and spent Rs. 500 for its carriage.
Jan 15 Paid Rs. 20,000 for cement, Rs. 10,000 for timber and Rs. 5,000 as wages for the construction of building.
Jan 17 Purchased an old machinery for Rs. 20,000 and spent Rs. 2,500 on its immediate repair.
Jan 20 Paid Rs. 500 to repairing some other machinery.
Solution 16:
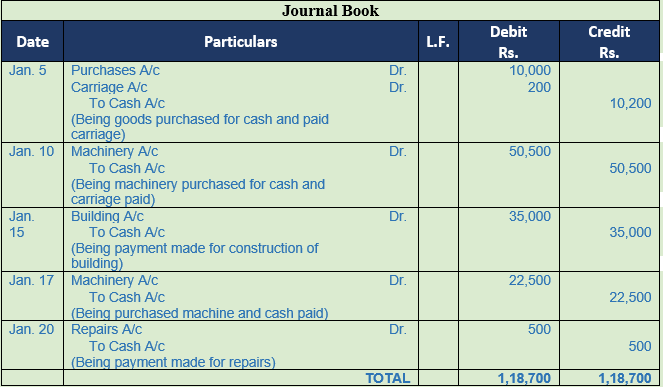
Question 17. Pass Journal Entries
2016
June 1 Arun Govil & Co. paid into bank as capital Rs. 6,00,000
June 3 Purchased goods from Mukesh of the list price of Rs. 2,00,000 at 10% trade discount
June 4 One-fourth of the above goods returned to Mukesh for not being upto specifications
June 6 Issued a cheque to Mukesh for the amount due to him after deducting 2% as cash discount
June 7 Withdrew from bank Rs. 2,50,000 for office use and Rs. 10,000 for personal use
June 10 Purchased a machinery for Rs. 1,00,000 and spent Rs. 5,000 on its installation. Payment for machinery was made by cheque and installation expenses were paid in cash
June 12 Sold goods for Rs. 1,00,000 to Amar
June 13 Amar clears his account by giving a cheque of Rs. 98,500. Cheque is immediately sent to bank
June 15 Purchased stationery for personal use Rs. 3,000 and for office use Rs. 5,000
June 20 Purchased land for Rs. 2,00,000 and paid 1% as brokerage and Rs. 15,000 as registration charges on it. Entire payment is made by Cheque
June 30 Wages due to labourers Rs. 20,000 and salary due to the clerk Rs. 30,000
Solution 17:
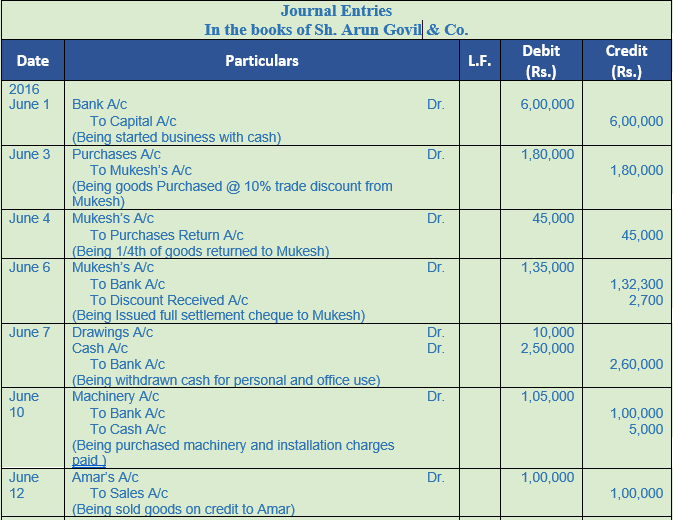
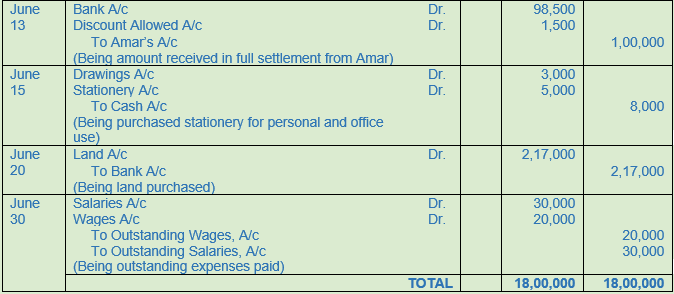
Question 18. Pass Journal Entries
- Purchased timber from Kuldeep Kumar, for cash Rs. 2,000 and credit Rs. 10,000.
- Paid to Kuldeep Kumar in full settlement of his account Rs. 9,950.
- Paid rent in advance Rs. 10,000.
- Purchased machinery for Rs. 1,00,000 by cheque and carriage Rs. 2,000 and installation charges Rs. 1,000 paid in Cash.
- Purchased goods for Rs. 50,000 from Govind and sold it to Manohar for Rs. 65,000.
Solution 18:
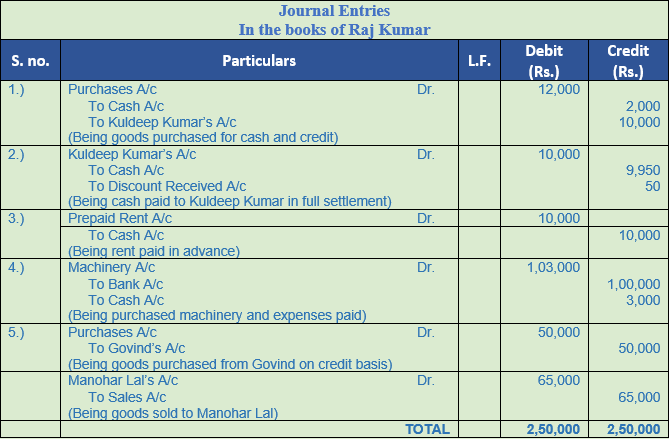
Point of Knowledge:-
Cash Discount allowed is debited to ‘Discount Allowed Account’ by the party receiving the amount and cash discount received is credited to ‘Discount Received Account’ by the party making the payment. Discount allowed or received is related to payment and thus, they are recorded in the books of account along with the entry recorded for payment and receipt of the amount, in cash or cheque. When cash discount is allowed or received GST or CGST, SGST, IGST is not levied since it is for early payment and not on sale or purchase of goods.
Question 19. Pass Journal Entries
- Purchased Machinery for Rs. 20,000 and paid Rs. 200 for its carriage.
- Received a cheque for Rs. 4,850 from X in full settlement of his account of Rs. 5,000. Cheque was immediately deposited into bank.
- Received by cheque a first and final payment of 60 paise in a Rs. from Y who owed us Rs. 10,000.
- Sold goods to Z for Rs. 10,000 at a trade discount of 20%. Next day a cheque was received from him after deducting 5% cash discount. Cheque was immediately deposited into Bank.
- Goods costing Rs. 20,000 sold to Manoj at a profit of 20% on cost less 10% trade discount.
Solution 19:
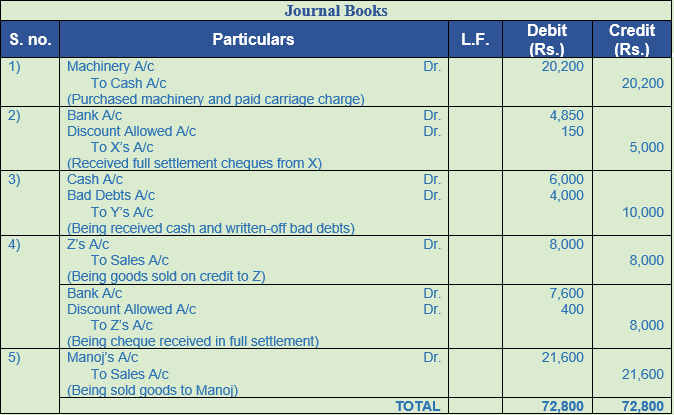
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 10,000
Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 10,000 × 20% = Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 10,000 – Rs. 2,000
Sales = Rs. 8,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 8,000 × 5%
= Rs. 400
Amount Received = Rs. 8,000 – Rs. 400
= Rs. 7,600
Point of Knowledge:-
Discount allowed or received is related to payment and thus, they are recorded in the books of account along with the entry recorded for payment and receipt of the amount, in cash or cheque. When cash discount is allowed or received GST or CGST, SGST, IGST is not levied since it is for early payment and not on sale or purchase of goods.
Question 20. Pass Journal Entries
1. Goods for Rs. 50,000 were destroyed by fire.
2. Goods worth Rs. 18,000 were distributed as free samples and Rs. 20,000 were given away as charity in cash.
3. Goods worth Rs. 25,000 and cash Rs. 40,000 were taken away by the proprietor for his personal use.
4. Goods worth Rs. 20,000 and cash Rs. 5,000 were given away as charity.
5. Cash Rs. 1,00,000 were stolen from the Iron Safe of the trader.
Solution 20:
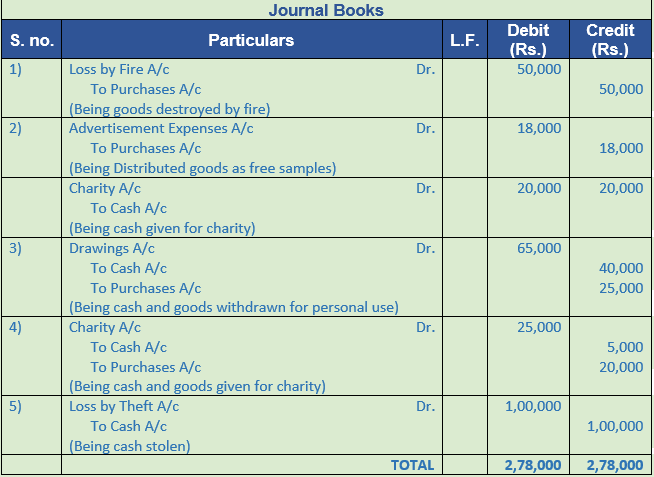
Point of Knowledge:-
1. Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
2. Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
3. Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
4. Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
Question 21: Pass Journal Entries
1. Sold goods to Brijesh of the list price of Rs. 10,000 at trade discount of 5%. Received full payment in cash.
2. Goods given away as charity Rs. 1,000.
3. Charge interest on capital of Rs. 5,00,000 @ 7% p.a.
4. Outstanding wages Rs. 3,000.
5. Rs. 5,000 due from Sunny are now bad debts.
6. Rs. 50,000 cash sales (of goods costing Rs. 40,000).
Solution 21:
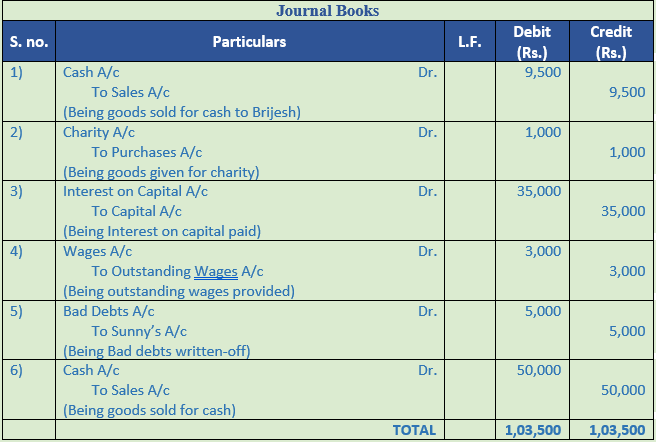
Question 22. Pass Journal Entries
(a) Proprietor withdrew for private use Rs. 10,000 from bank.
(b) Goods costing Rs. 50,000 were burnt by fire.
(c) Purchased machinery for cash Rs. 1,50,000 and paid Rs. 2,000 on its installation.
(d) Charge 5% depreciation on building costing Rs. 2,00,000 and 8% depreciation on furniture costing Rs. 5,000.
(e) Prepaid salary Rs. 2,000.
(f) Kapil who owed us Rs. 20,000 becomes insolvent and nothing is received from his estate.
Solution 22:
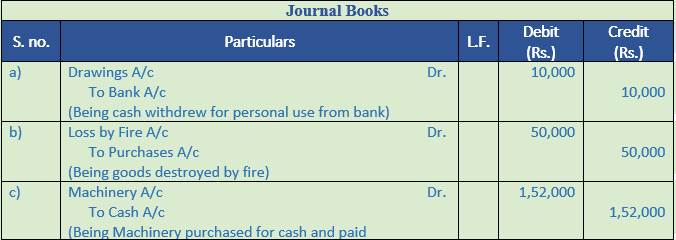
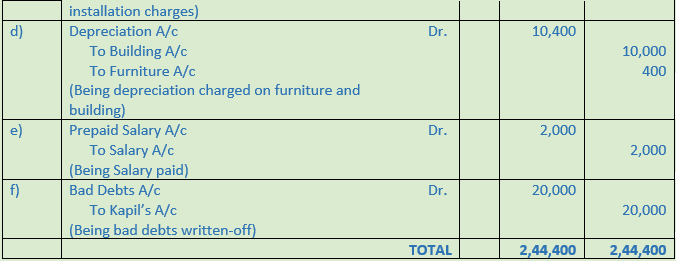
Point of Knowledge:-
1.) To record transactions of a particular head.
2.) To record the amount of a particular transaction.
3.) The record the effect of a transaction.
4.) To record the direction of a transaction.
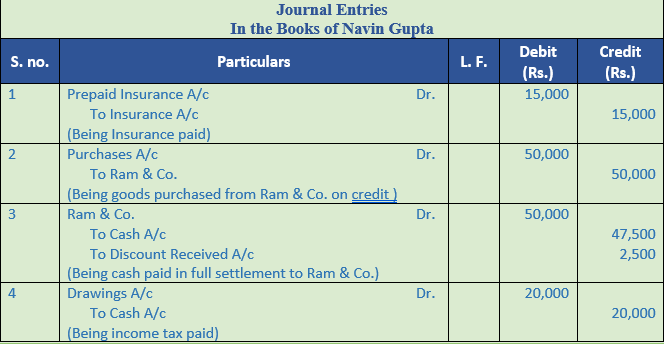
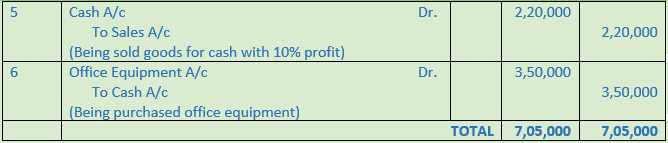
Question 23. Record Navin Gupta & Sons Journal Entries
1. Out of Insurance premium paid this year, Rs. 15,000 is related to next year.
2. Credit purchases from Ram & Co. for Rs. 50,000. Cash discount will be received at 5% on payment of bill within 10 days.
3. Cash paid to Ram & Co. and discount availed of.
4. Paid Income Tax Rs. 20,000 by cheque.
5. Goods costing Rs. 2,00,000 sold for cash at a profit of 10%.
6. Purchased iron safe for Rs. 2,00,000 filing cabinet for Rs. 50,000 and Computer for Rs. 1,00,000.
Solution 23:
Question 24. Record journal book of Kanishk Traders
1. Sold goods costing Rs. 1,20,000 to Charu at a profit of 33 % on cost less 15% Trade Discount.
2. Sold goods costing Rs. 80,000 to Arun against cheque at a profit of 25% on cost less 15% Trade Discount.
3. Paid by cheque Rs. 8,400 as insurance premium for a period of 12 months starting 1st August 2016. Financial year closes on 31st March every year.
Solution 24:
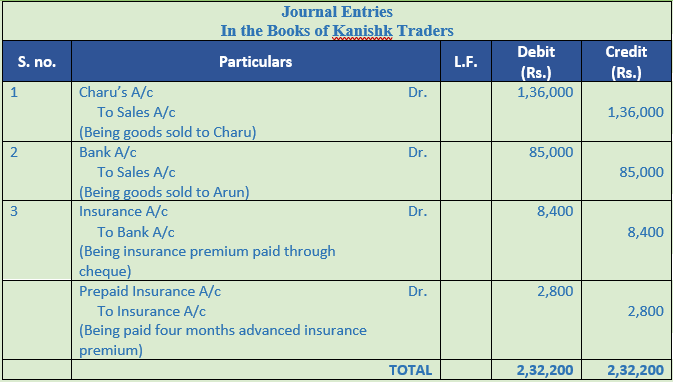
Question 25. Record journal book
2017
March Particulars
4 Purchased building for Rs. 1,50,000 and incurred expenses of Rs. 10,000 on its purchase
10 Satish who owed us Rs. 20,000 is declared insolvent and 60 paise per Rs. is received from his estate
15 Paid Rs. 500 for repairing the office furniture
18 Proprietor withdrew for his personal use cash Rs. 5,000 and goods worth Rs. 2,000
20 Purchased the following items for business. Iron Safe Rs. 15,000; Filing Cabinet Rs. 5,000; Computer Rs. 12,000; Postage Rs. 200 and Stationery Rs. 150
28 Paid electricity charges Rs. 1,600
31 Charge depreciation on Machinery @ 10% for one year (Machinery Rs. 75,000)
31 Outstanding wages at the end of the year Rs. 6,000
Solution 25:
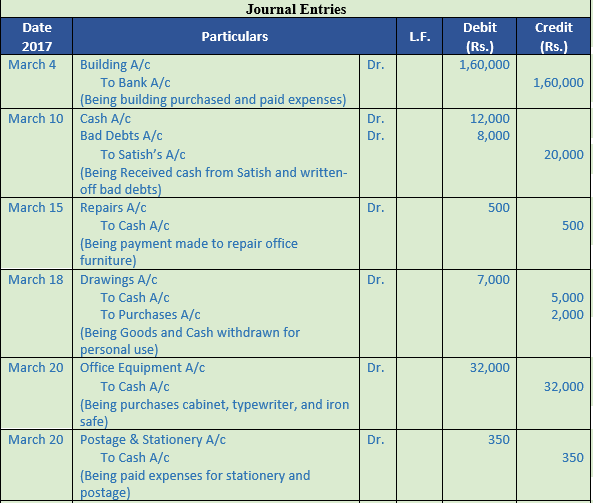
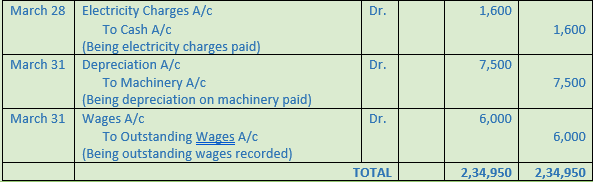
Question 26. Record journal book
1. Purchased goods for Rs. 25,000 for Cash and paid Rs. 200 for carriage on these goods.
2. Purchased goods for Rs. 40,000 on Credit from Sudhir and paid Rs. 500 for carriage on these goods.
3. Purchased machinery for Rs. 20,000 and spent Rs. 500 on its carriage and Rs. 300 on its installation.
4. Purchased goods from Anil for Rs. 15,000.
5. Sold 1/3 rd of the above goods at a profit of 20% on cost.
6. Goods costing Rs. 12,000 sold to Mr. X, issued invoice at 25% above cost less 10% trade discount.
7. Provide 20% depreciation on furniture costing Rs. 10,000.
8. Gave as charity − Cash Rs. 500 and Goods Rs. 2,000.
Solution 26:
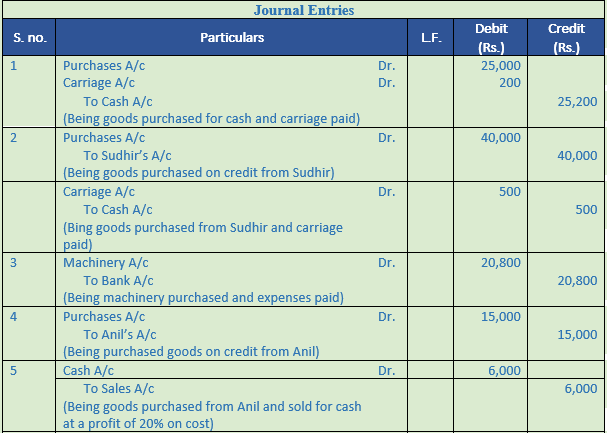
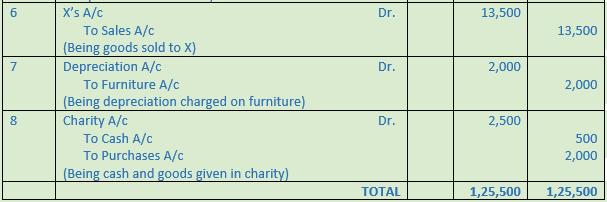
Question 27. Record journal book
1. Received a V.P.P. from Mohan Lal for Rs. 25,000. Sent a peon to collect it who paid Rs. 200 as cartage
2. Received Rs. 1,000 from sales of old newspapers and Rs. 5,000 from sales of old chairs
3. Goods given away as charity goods costing Rs. 7,000
4. Received Cash from a debtor written off as bad-debt last year Rs. 20,000
5. Sold goods costing Rs. 50,000 to Ashok on credit at a profit of 20% on cost
6. Sold goods costing Rs. 1,00,000 for Rs. 1,40,000
7. Provide Rs. 50,000 as interest on Capital
8. Paid rent of building Rs. 60,000 by cheque. Half the building is used by the proprietor for residential purpose
9. Outstanding salary at the end of the year Rs. 30,000
Solution 27:
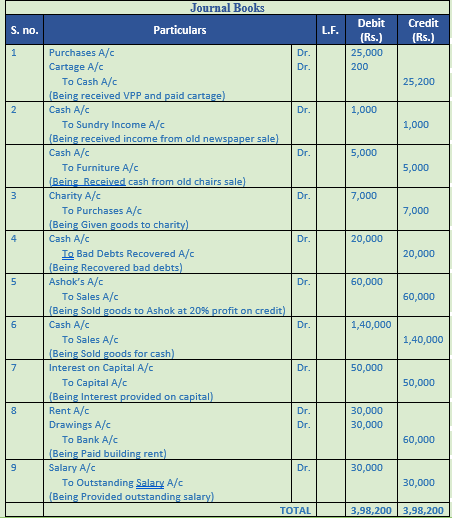
Question 28. Record journal book
2018 Particulars
April 1 Purchased goods for Rs. 1,00,000 from Manoj and availed discount of Rs. 10,000
April 2 Paid amount due to Manoj by cheque and availed discount of Rs. 4,500
April 5 Cash Rs. 5,000 paid to Desai and discount allowed by him Rs. 200
April 10 Cash Rs. 10,000 received from Govardhan and allowed him discount Rs. 500
April 12 Sold personal Car of the proprietor for Rs. 80,00 against cheque, which was deposited into the firm’s bank account
April 16 Sold personal Car of the proprietor for Rs. 1,50,000 against cheque, which was deposited into the proprietor’s personal bank account
April 20 Sold goods to Gaurav costing Rs. 1,00,000 at a profit of 40% and allowed him 10% trade discount and paid for cartage Rs. 3,000 not to be charged from him
April 24 Placed an order with Rudra & Co. for supply of goods of Rs. 80,000 and a cheque for 40% amount is sent to them as an advance
Solution 28:
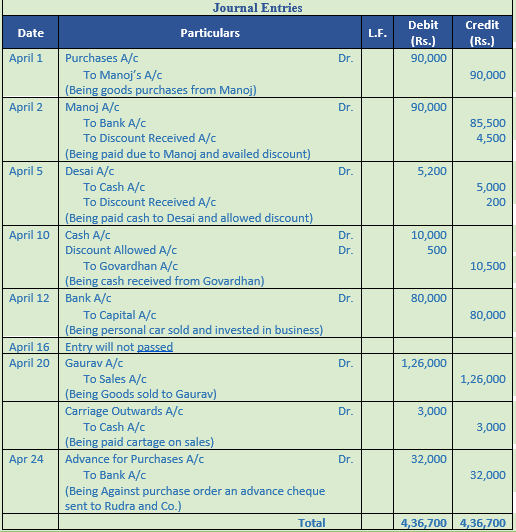
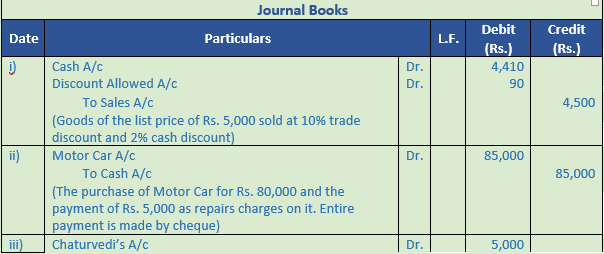
Question 29. Give the journal entries corresponding to the narration given below:-
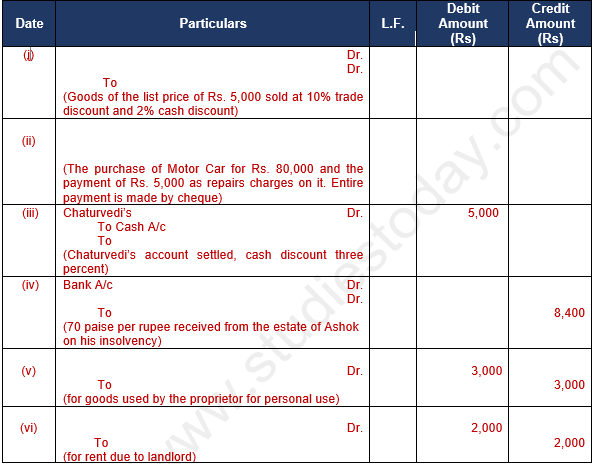
Solution 29:
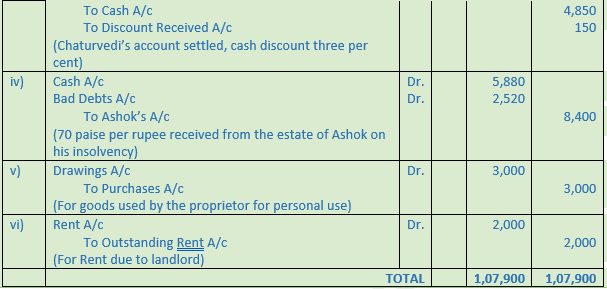
Question 30. Rectify the following entries assuming that the narration in each case is correct
Solution 30:
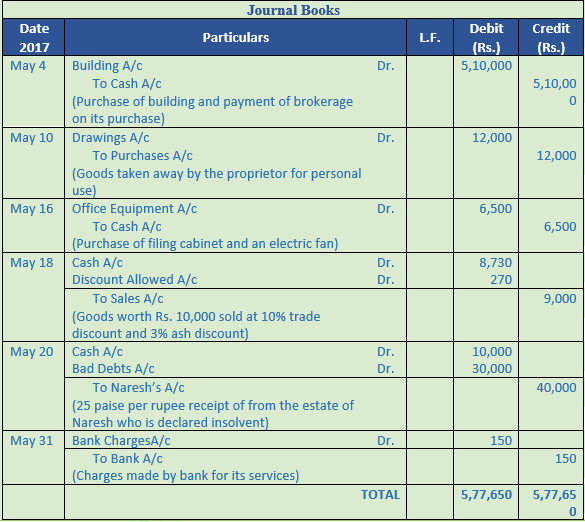
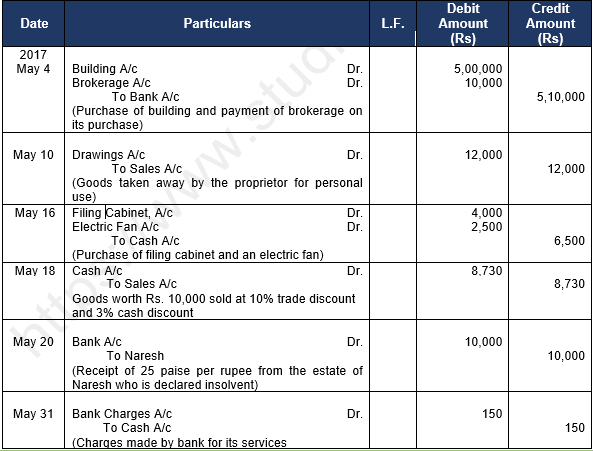
Question 31. Record journal book
S no. Particulars
1 Goods destroyed by Fire for Rs. 5,000
2 Paid by cheque Rs. 25,000 as wages on installation of a Machinery
3 Issued a cheque in favour of M/s Parmatma Saran & Sons on account of purchase of goods Rs. 75,000
4 Goods sold costing Rs. 60,000 to M/s Kalu Sons at an invoice price 10% above cost less 5% Trade discount
Solution 31:
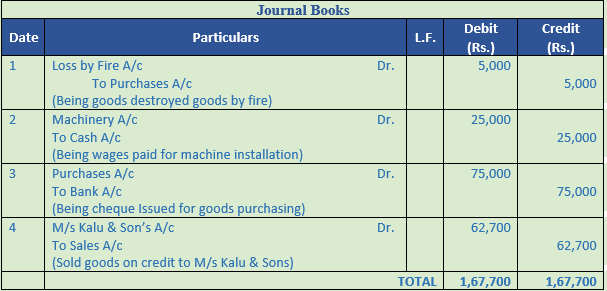
Working Note:-
Calculation Selling price of the goods sold to M/s Kalu & Sons
Cost = Rs. 60,000
Profit = Rs. 60,000 × 10%
= Rs. 6,000
List Price = Cost price + Profit
= Rs. 60,000 + Rs. 6,000
= 66,000
Trade discount = 5%
Trade discount = List Price × % of trade discount
= Rs. 66,000 × 5%
= Rs. 3,300
Sale price = List Price – Trade discount
= 66,000 – 3,300
= 62,700
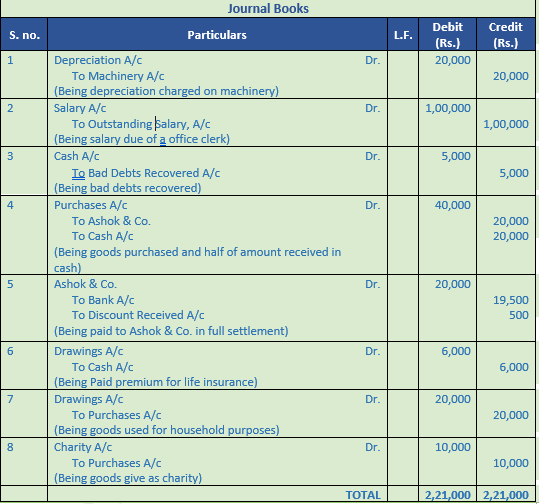
Question 32. Record journal book
Journalise the following transactions:−
S no. Particulars (Rs.)
1. Charge depreciation on Machinery 20,000
2. Salary due to Office Clerks 1,00,000
3. Received cash for Bad-Debts written off last year 5,000
4. Purchased goods from Ashok & Co. for Rs. 50,000 at 20%
rade Discount. Half the payment was made in cash.
5. Issued cheque to Ashok & Co. in full settlement 19,500
6. Paid Life Insurance Premium by cheque 6,000
7. Proprietor used goods for household purposes 20,000
8. Goods given free to a hospital out of business 10,000
Solution 32:
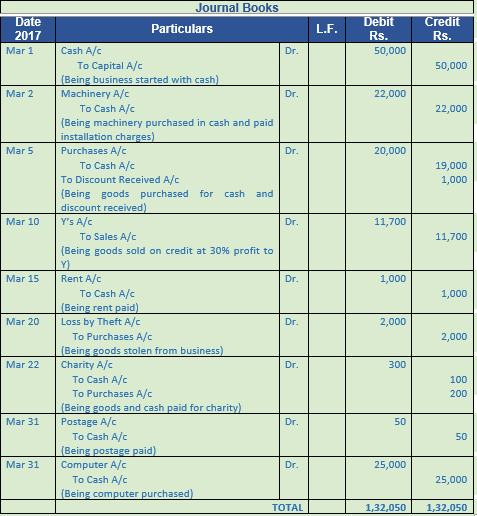
Question 33. Record journal book
2017
March Particulars (Rs.)
1 Started business with cash 50,000
2 Purchased Machinery for cash 20,000
Paid installation charges on machinery 2,000
5 Purchased goods from X of the list price of Rs. 25,000, Trade Discount 20%
and cash discount 5%. Payment was made in cash immediately.
10 Sold goods to Y costing Rs. 10,000 at 30% profit on cost less 10% trade discount.
15 Paid Rent 1,000
20 Goods stolen from business 2,000
22 Gave as charity : Cash 100
Goods 200
31 Purchased Post Cards and Envelopes 50
31 Purchased a Computer for business 25,000
Solution 33:
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 25,000
Trade Discount = 20%
Trade Discount = Rs. 25,000 × 20% = Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 25,000 – Rs. 5,000
Sales = Rs. 20,000
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 20,000 × 5%
= Rs. 1,000
Amount Received = Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 1,000
= Rs. 19,000
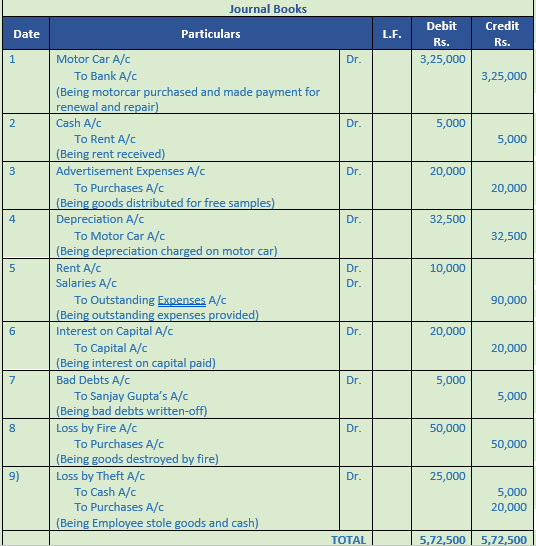
Question 34. Record journal book
1. Purchased a Motor Car for Rs. 3,00,000 and paid Rs. 25,000 for its repair and renewal. Entire payment is made by cheque.
2. Received Rent Rs. 5,000.
3. Goods worth Rs. 20,000 were distributed as free samples.
4. Charge depreciation on Motor Car Rs. 32,500.
5. Rent due to Landlord Rs. 10,000 and Salary due to Clerks Rs. 80,000.
6. Charge interest on Capital Rs. 20,000.
7. Rs. 5,000 due from Sanjay Gupta are bad-debts.
8. Goods worth Rs. 50,000 were destroyed by fire.
9. Cash Rs. 5,000 and goods worth Rs. 20,000 were stolen by an employee.
Solution 34:
Question 35. Journalise the following transactions:
(i) Bought goods from Arun for Rs. 2,00,000 at a trade discount of 15% and cash discount of 2%. Paid 80% amount immediately.
(ii) Purchased foods for Rs. 20,000 from X and supplied it to Y for Rs. 26,000.
(iii) Cash withdrawn from bank Rs. 5,000 for personal use and Rs. 25,000 for office use.
(iv) Goods destroyed by fire : Cost Price Rs. 40,000.
(v) Provide 20% depreciation on machinery costing Rs. 50,000.
(vi) Out of insurance paid this year, Rs. 3,000 is related to next year.
(vii) Allow Rs. 5,000 as interest on capital and charge Rs. 1,000 as interest on drawings.
(viii) Sohan who owed us Rs. 25,000 was declared insolvent and a cheque of 40 paise in a Rs. is received from him in full settlement.
(ix) Paid Income Tax Rs. 10,000 by cheque.
(x) Salary paid Rs. 80,000 and Salary Outstanding Rs. 20,000.
Solution 35:
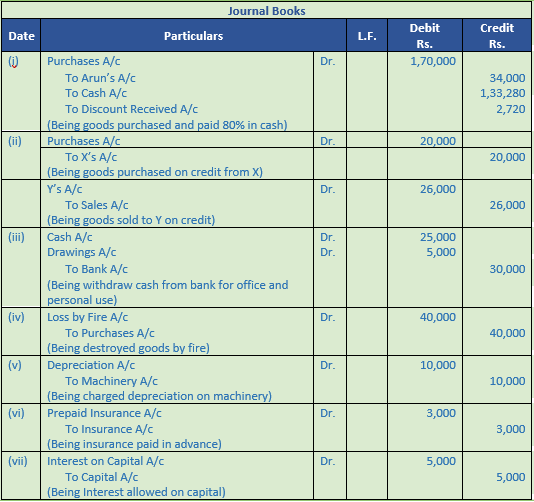
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 2,00,000
Trade Discount = 15%
Trade Discount = Rs. 2,00,000 × 15% = Rs. 30,000
Sales = Rs. 2,00,000 – Rs. 30,000
Sales = Rs. 1,70,000
Cash Received = 1,70,000 × 80%
= Rs. 1,36,000
Cash discount = 2%
Discount amount = Rs. 1,36,000 × 2%
= Rs. 2,720
Amount Received = Rs. 1,36,000 – Rs. 2,720
= Rs. 1,33,280
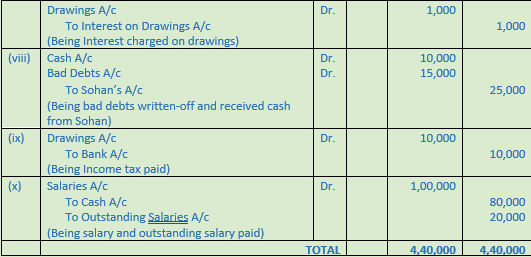
Question 36. Journalise the following transactions:
2017
March Particulars
1 Purchased a Machinery for Rs. 1,00,000 and the payment was made by issuing a cheque from Proprietor’s saving bank account.
4 Received an order from Chakravarti for goods of Rs. 4,00,000 along with a cheque of 10% of the order as advance.
8 Paid cash Rs. 8,000 to Dushyant and discount allowed by him Rs. 800.
10 Goods were stolen by an employee (Sale Price Rs. 20,000; Cost Rs. 15,000).
15 Purchased stationery worth Rs. 8,000 for office use and Rs. 2,000 for personal use.
20 Manoj pays us Rs. 5,400 after deducting 10% for prompt payment.
28 Sold goods to Kuber costing Rs. 2,00,000 at 25% above cost less trade discount of 10% and cash discount of 5%. Kuber did not avail the cash discount.
Solution 36:
Point of Knowledge:-
1. Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
2. Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
3. Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
4. Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
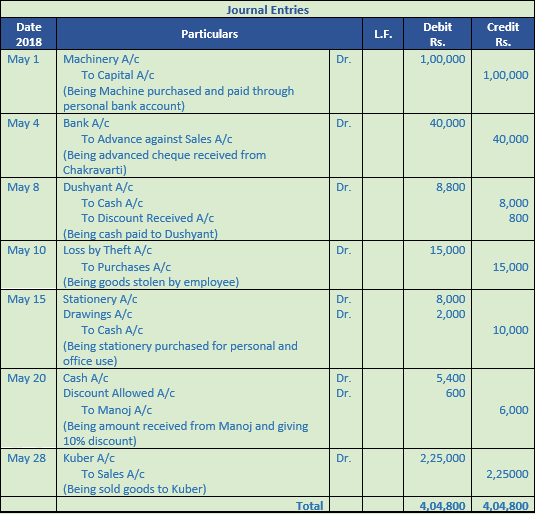
Question 37. Prepare journal
(a) Goods worth Rs. 2,000 destroyed by fire.
(b) Received Rs. 5,000 from Suresh which were written off as bad debts.
(c) Sold goods to Mohan of the list price of Rs. 5,000 subject to 10% trade discount and 5% cash discount. Mohan availed cash discount.
(d) Received Rs. 9,900 from Hari in full settlement of his account Rs. 10,000.
Solution 37:
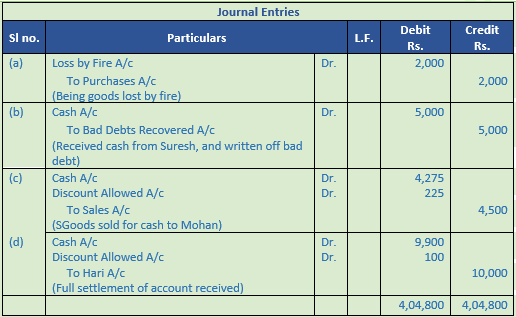
Working Note:-
List price = Rs. 5,000
Trade Discount = 10%
Trade Discount = Rs. 5,000 × 10% = Rs. 500
Sales = Rs. 5,000 – Rs. 500
Sales = Rs. 4,500
Cash discount = 5%
Discount amount = Rs. 4,500 × 5%
= Rs. 225
Amount Received = Rs. 4,500 – Rs. 225
= Rs. 4,275
Point of Knowledge:-
- Recording of accounting data in chronological order.
- Narration of journal explains the transactions very well.
Question 38. Prepare a journal for the following transaction of Vibha and Co.

Solution 38:
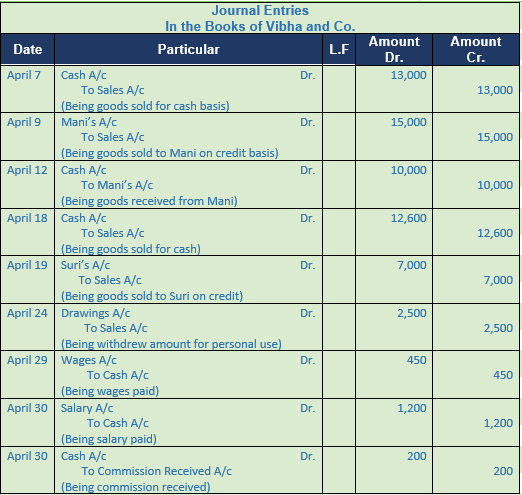
Point of knowledge:-
A Liability Account is credited when there is an increase in liability. We will debit the liability account to reduce the balance.
The example to reduce a liability account is paid outstanding rent Rs. 1000. The Outstanding Rent Account will be debited by Rs. 1000.
Question 39. Record the following transactions in the journal of Vimal Bros.

Solution 39:
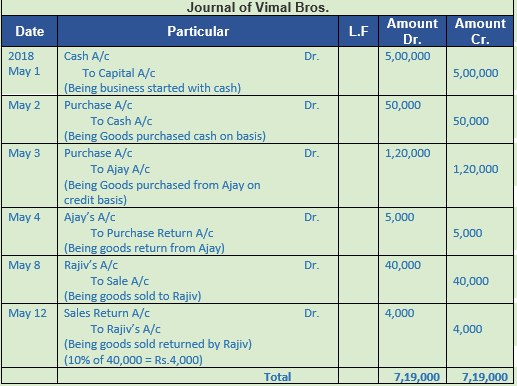
Point of Knowledge:-
- Asset Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
- Liability Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Capital Accounts: Debit the decreases, Credit the increases.
- Expense Accounts: Debit the increases, Credit the decreases.
