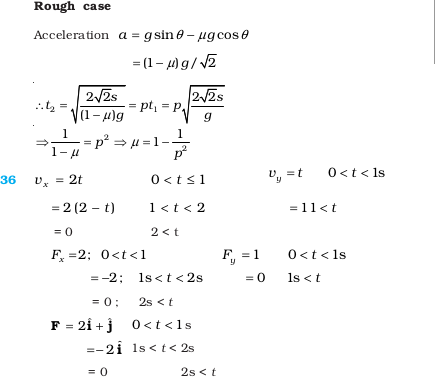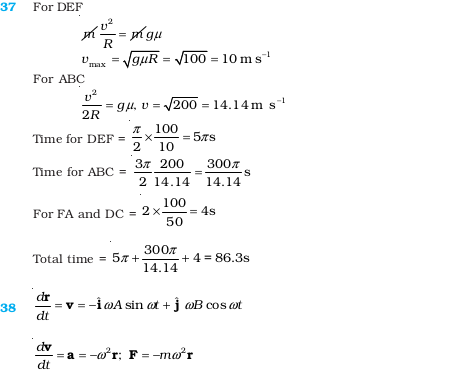NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 4: Laws of Motion. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Laws of Motion prepare students for their Class 11 exams thoroughly.
Physics problems and solutions for the Class 11 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
Contents
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 4: Laws of Motion
Class 11: Physics Chapter 4 solutions. Complete Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Notes.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ I)
- A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This means that
- (a) it is at rest.
- (b) the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform speed.
- (c) all parts of the ball have the same velocity (magnitude and direction) and the velocity is constant.
- (d) the centre of the ball moves with constant velocity and the ball spins about its centre uniformly.
- A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies
- (a) the force acting on the scale is zero, but a torque about the centre of mass can act on the scale.
- (b) the force acting on the scale is zero and the torque acting about centre of mass of the scale is also zero.
- (c) the total force acting on it need not be zero but the torque on it is zero.
- (d) neither the force nor the torque need to be zero.


- In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is
- (a) Zero
- (b) 0.75 kg m s–1
- (c) 1.5 kg m s–1
- (d) 14 kg m s–1
- Conservation of momentum in a collision between particles can be understood from
- (a) conservation of energy.
- (b) Newton’s first law only.
- (c) Newton’s second law only.
- (d) both Newton’s second and third law.
- A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is
- (a) frictional force along westward.
- (b) muscle force along southward.
- (c) frictional force along south-west.
- (d) muscle force along south-west.
- A body of mass 2kg travels according to the law x(t ) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms-1, q = 4 ms-2 and r = 5 ms-3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is
- (a) 136 N
- (b) 134 N
- (c) 158 N
- (d) 68 N
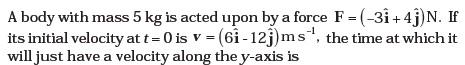
- (a) never
- (b) 10 s
- (c) 2 s
- (d) 15 s


Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ II)
- The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x( t ) = A sin 4p t for 0 < t <(1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t >(1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- (a) The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is –16π2 A m.
- (b) The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- (c) The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- (d) The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- (e) There is no impulse acting on the particle.
- In Fig. 5.1, the co-efficient of friction between the floor and the body B is 0.1. The co-efficient of friction between the bodies B and A is 0.2. A force F is applied as shown on B. The mass of A is m/2 and of B is m. Which of the following statements are true?
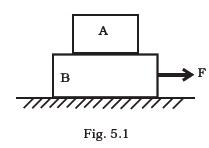
- (a) The bodies will move together if F = 0.25 mg.
- (b) The body A will slip with respect to B if F = 0.5 mg.
- (c) The bodies will move together if F = 0.5 mg.
- (d) The bodies will be at rest if F = 0.1 mg.
- (e) The maximum value of F for which the two bodies will move together is 0.45 mg.
- Mass m1 moves on a slope making an angle θ with the horizontal and is attached to mass m2 by a string passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in Fig. 5.2. The co-efficient of friction between m1 and the sloping surface is μ.
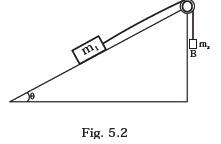
Which of the following statements are true?- (a) If m2 > m1 sinθ , the body will move up the plane.
- (b) If m2 > m1 sinθ + μ cosθ , the body will move up the plane.
- (c) If m2 < m1 sinθ + μ cosθ , the body will move up the plane.
- (d) If m2 < m1 sinθ − μ cosθ , the body will move down the plane.
- In Fig. 5.3, a body A of mass m slides on plane inclined at angle θ1 to the horizontal and μ1 is the coefficient of friction between A and the plane. A is connected by a light string passing over a frictionless pulley to another body B, also of mass m, sliding on a frictionless plane inclined at angle θ2 to the horizontal. Which of the following statements are true?

- (a) A will never move up the plane.
- (b) A will just start moving up the plane when
μ = sin θ2 – sin θ1 / cos θ1 - (c) For A to move up the plane, θ2 must always be greater than θ1 .
- (d) B will always slide down with constant speed.
- Two billiard balls A and B, each of mass 50g and moving in opposite directions with speed of 5m s-1 each, collide and rebound with the same speed. If the collision lasts for 10-3 s, which of the following statements are true?
- (a) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg m s-1 and the force on each ball is 250 N.
- (b) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg m s–1 and the force exerted on each ball is 25 × 10–5 N.
- (c) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.5 Ns.
- (d) The impulse and the force on each ball are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6N and 8N. The resultant acceleration of the body is
- (a) 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan-1 (4 / 3) w.r.t. 6N force.
- (b) 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan-1 (4 / 3) w.r.t. 6N force.
- (c) 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan-1 (3 / 4) w.r.t. 8N force.
- (d) 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan-1 (3 / 4) w.r.t. 8N force.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
- A girl riding a bicycle along a straight road with a speed of 5 m s–1 throws a stone of mass 0.5 kg which has a speed of 15 m s–1 with respect to the ground along her direction of motion. The mass of the girl and bicycle is 50 kg. Does the speed of the bicycle change after the stone is thrown? What is the change in speed, if so?
- A person of mass 50 kg stands on a weighing scale on a lift. If the lift is descending with a downward acceleration of 9 m s-2, what would be the reading of the weighing scale? (g = 10 m s-2 )
- The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in Fig. 5.4. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

- A person driving a car suddenly applies the brakes on seeing a child on the road ahead. If he is not wearing seat belt, he falls forward and hits his head against the steering wheel. Why?

- A block placed on a rough horizontal surface is pulled by a horizontal force F. Let f be the force applied by the rough surface on the block. Plot a graph of f versus F.
- Why are porcelain objects wrapped in paper or straw before packing for transportation?
- Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
- A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 m s1.
- (a) What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- (b) If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
- Why are mountain roads generally made winding upwards rather than going straight up?
Short Answer Type Questions
- A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB (Fig. 5.5). Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually, harder and harder in the downward direction so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?
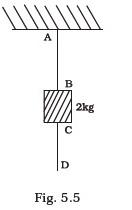
- In the above given problem if the lower thread is pulled with a jerk, what happens?
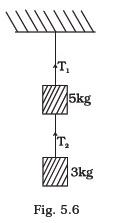
- Two masses of 5 kg and 3 kg are suspended with help of massless inextensible strings as shown in Fig. 5.6. Calculate T1 and T2 when whole system is going upwards with acceleration = 2 m s2 (use g = 9.8 m s-2 ).
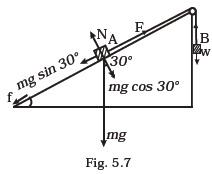
- Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (Fig. 5.7). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictionless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.
- A block of mass M is held against a rough vertical wall by pressing it with a finger. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is μ and the acceleration due to gravity is g, calculate the minimum force required to be applied by the finger to hold the block against the wall ?
- A 100 kg gun fires a ball of 1kg horizontally from a cliff of height 500m. It falls on the ground at a distance of 400m from the bottom of the cliff. Find the recoil velocity of the gun. (acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s–2)
- Figure 5.8 shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.

- If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.
- A person in an elevator accelerating upwards with an acceleration of 2 m s–2, tosses a coin vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s1. After how much time will the coin fall back into his hand? ( g = 10 m s–2)
Long Answer Type Questions
- There are three forces F1, F2 and F3 acting on a body, all acting on a point P on the body. The body is found to move with uniform speed.
- (a) Show that the forces are coplanar.
- (b) Show that the torque acting on the body about any point due to these three forces is zero
- When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
- Figure 5.9 shows (vx ,t ),and(vy,t ) diagrams for a body of unit mass. Find the force as a function of time.

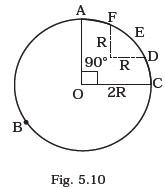
- A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Fig. 5.10). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-effecient of friction on the road is μ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 m s-1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

- (a) Show that the trajectory is an ellipse.
- (b) Show that F = −mω2r.
- A cricket bowler releases the ball in two different ways
- (a) giving it only horizontal velocity, and
- (b) giving it horizontal velocity and a small downward velocity.
- The speed vs at the time of release is the same. Both are released at a height H from the ground. Which one will have greater speed when the ball hits the ground? Neglect air resistance.
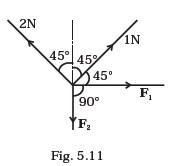
- There are four forces acting at a point P produced by strings as shown in Fig. 5.11, which is at rest. Find the forces F1 and F2 .
- A rectangular box lies on a rough inclined surface. The co-efficient of friction between the surface and the box is μ. Let the mass of the box be m.
- (a) At what angle of inclination θ of the plane to the horizontal will the box just start to slide down the plane?
- (b) What is the force acting on the box down the plane, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased to α > θ ?
- (c) What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box either remain stationary or just move up with uniform speed?
- (d) What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box move up the plane with acceleration a?
- A helicopter of mass 2000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The total mass of the crew and passengers is 500 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the (g = 10 m s–2)
- (a) force on the floor of the helicopter by the crew and passengers.
- (b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air.
- (c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
Answers to Multiple Choice Questions