NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 14: Statistics and Probability. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics and Probability prepare students for their Class 9 exams thoroughly.
Maths problems and solutions for the Class 9 pdf are provided here which are similar to the questions being asked in the previous year’s board.
Contents
- 1 NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 14: Statistics and Probability
- 1.1 Main Concepts and Results
- 1.2 Multiple Choice Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.3 Multiple Choice Questions
- 1.4 Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
- 1.5 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Solved Examples)
- 1.6 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)
- 1.7 Short Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.8 Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
- 1.9 Long Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)
- 1.10 Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
- 1.11 Answers
- 1.12 Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)
- 1.13 Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)
- 1.14 Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
- 1.15 Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 14: Statistics and Probability
Class 9: Maths Chapter 14 solutions. Complete Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Notes.
Main Concepts and Results
Statistics
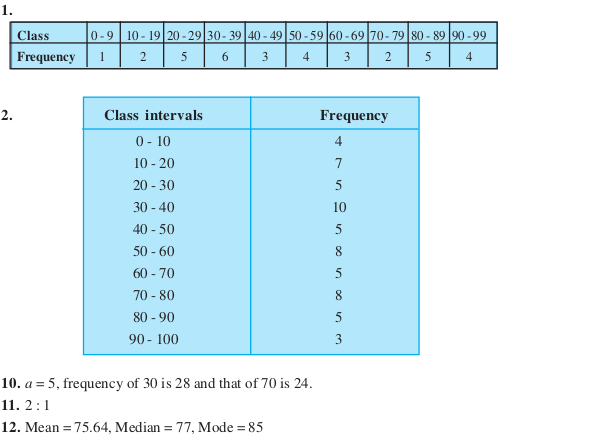
Meaning of ‘statistics’, Primary and secondary data, Raw/ungrouped data, Range of data, Grouped data-class intervals, Class marks, Presentation of data – frequency distribution table, Discrete frequency distribution and continuous frequency distribution.
- Graphical representation of data :
(i) Bar graphs
(ii) Histograms of uniform width and of varying widths
(iii) Frequency polygons - Measures of Central tendency
(a) Mean
(i) Mean of raw data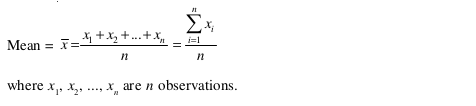
(ii) Mean of ungrouped data
(b) Median
A median is the value of the observation which divides the data into two equal parts, when the data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order.
Calculation of Median
When the ungrouped data is arranged in ascending (or descending) order, the median of data is calculated as follows :
(c) Mode
The observation that occurs most frequently, i.e., the observation with maximum frequency is called mode. Mode of ungrouped data can be determined by observation/ inspection.
Probability
- Random experiment or simply an experiment
- Outcomes of an experiment
- Meaning of a trial of an experiment
- The experimental (or empirical) probability of an event E (denoted by P(E)) is given by
P(E) = Number of trials in which the event has happened / Total number of trials - The probability of an event E can be any number from 0 to 1. It can also be 0 or 1 in some special cases.
Multiple Choice Questions (Solved Examples)

Multiple Choice Questions

Short Answer Questions with Reasoning

Short Answer Type Questions

Long Answer Type Questions
Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)

Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Solved Examples)

Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)

Short Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)



Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)

Long Answer Type Questions (Solved Examples)



Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)

Answers
Multiple Choice Questions (Exercise)

Short Answer Questions with Reasoning (Exercise)


Short Answer Type Questions (Exercise)



Long Answer Type Questions (Exercise)